Digitalization continues unabated and is permeating all sectors of the economy, including the automotive industry. As a result, cars have become rolling computers, the laptop has found its way into the workshop, and IT security has become a relevant development goal. This brings with it new opportunities – and, it must also be said of course, new types of error sources and cost risks. With the right strategies, however, an after-sales service can be made more efficient.
One of the possibilities opened up by the digital vehicle world is the remote improvement of vehicle functions using over-the-air updates (OTA). New digital twin-based service and management concepts for the repair shop should also be mentioned here. At the same time, enormous efforts must be made to ensure the security of systems, data and people in this digital and networked world.
In the following, we will use these examples to show how the digital vehicle environment gives rise to new aspects for after-sales service. Because digitalization creates not only convenience functions and greater flexibility in configuration: it can also be the cause of previously unknown faults, which might possibly make service more time-consuming and costly. With a partner like the EDAG Group, which combines broad domain knowledge with high-level digitalization expertise, you can derive maximum benefit from the digitalization of the vehicle environment while keeping after-sales costs under control.
Hassle-free OTA updates
Modern vehicles contain numerous software systems and assistants. Frequently, these use mobile communications technology to access data on the Internet – current route and traffic data for instance – or to transmit vehicle usage and health data, for fleet management, for example.
At the same time, data connections of this kind allow the manufacturer to update services and vehicle configurations, rectify faults, improve applications and add new functions. Over-the-air updates are a convenient means of installing software updates and patches in devices without an appointment at the repair shop – so a potential way of cutting costs.
The OTA concept is not, however, completely risk-free. If the update installed is not fully compatible, it can lead to loss of function – in the worst case, the vehicle will no longer start. There is also a risk of hackers gaining unauthorized access via the OTA interface. Another thing to take into account is the volume of the update. If large data quantities are transmitted to numerous devices at one and the same time, the network could become overloaded. In addition to high data transfer and server costs, this can also lead to slow transfer speeds and failed updates. 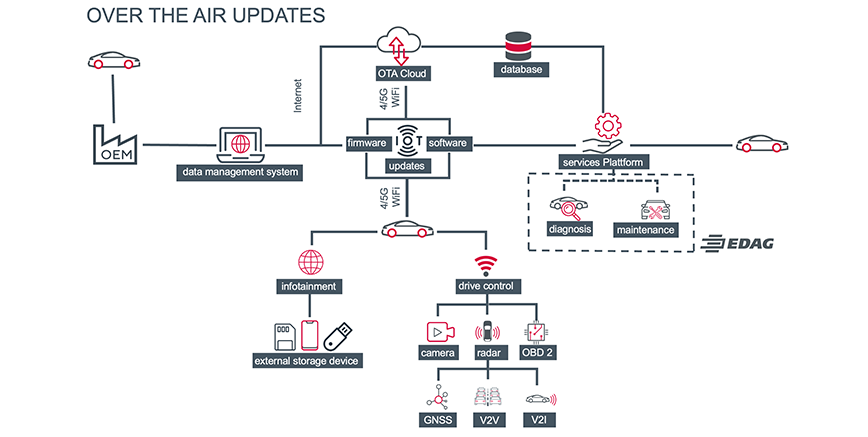
Problems with OTA updates often make it necessary for them to be reinstalled in the repair shop - at corresponding expense to both the customer and the service partner. Another effect is that battery defects have also been observed with increasing frequency, resulting in high repair or replacement costs.
This sets high requirements for the development of OTA updates, meaning that suitable tools need to be found and established processes adhered to, in order to ensure that the software updates are compatible with different hardware configurations and older vehicle models. Before the update is carried out, it must be tested to ensure it is fault-freed and working properly, to rule out any undesirable effects on the hardware. Security and privacy testing is also essential, as this guarantees that customers' data remains secure at every step of the update process.
In addition, the software must be optimized in such a way that the memory and network requirements remain as low as possible. By reducing the bandwidth and storage capacity required, manufacturers can cut costs and work more effectively. Smaller file sizes mean faster and more reliable transfer of data and therefore a lower error risk during the OTA update process.
EDAG specializes in the development of efficient OTA update solutions, to this end using innovative technologies and methods which are constantly being updated and improved. With the help of automated tools, OTA updates can be developed and implemented quickly and reliably. Close cooperation with manufacturers helps to ensure that updates run smoothly on different devices and platforms and that full compatibility is guaranteed. The use of secure transmission channels and encrypted communication minimizes the risk of cyber attacks or unauthorized access to either the network or the device.
However, the development environment must also be secured. The basic requirements are the use of robust technologies such as firewalls and virtual private networks (VPNs), and compliance with international standards and regulations through a systematically implemented functional safety management system. On request, experts with years of experience in the field of cybersecurity will provide assistance with the implementation of an effective cyber security management system (CSMS) which will meet the highest possible security standards, and with other security measures.
Digital twin outside of the factory
Unlike a digital 3D model, for example, a digital twin contains significantly more information about components, devices or plants. Geometry, kinematics and logic data, information on materials, functions, interfaces and a great deal more, through to data from operational use, for example the number of switching cycles of a relay. The concept of the digital twin is just taking off in industrial automation, albeit under a different name: Machines and systems there are being equipped with a "digital administration shell" or Asset Administration Shell (AAS).
Outside of the factory, however, the concept of the digital twin has so far frequently met with neglect – on occasion, even with hostility. Often, therefore, problems occurring on the road continue to be manually recorded, reported and analyzed, even though there are tried and tested technologies that could be used to avoid maintenance and repair cases or handle them with far greater efficiency.
Intelligent use of the digital twin can, for example, provide an additional digital database for optimizing repair shop processes. One aspect is the real-time monitoring of the availability of supplies and parts needed for future service jobs. Keeping a smart, digital inventory of workshop equipment - including existing tools - reduces time-consuming manual processes and helps to lessen the risk of theft. Although the implementation and acquisition of hardware and software for process optimization generates initial costs, these are amortized in a short time.
EDAG brings together various competencies that are needed for intelligent tool inventory using digital twins: Application know-how, process knowledge, software skills and conceptual strength, to name but a few. This results in a wide range of consulting, implementation and commissioning skills for such solutions. This could mean, for instance, for reviewing the situation and analyzing the current state, providing customization and inventory support, training employees and optimizing processes. 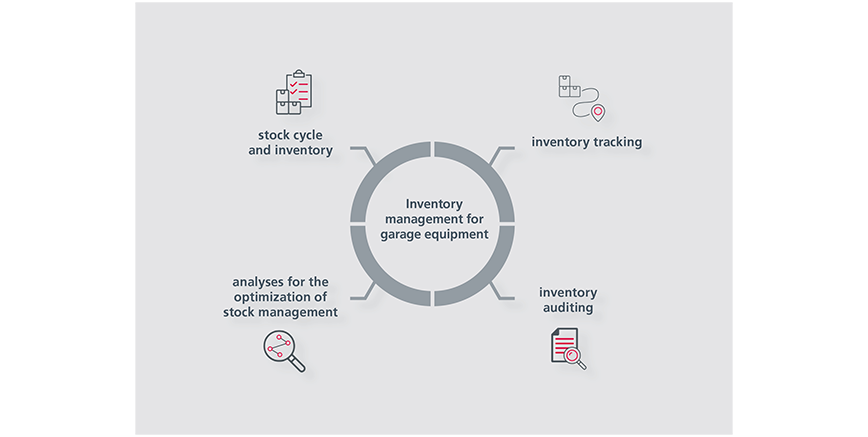
The same applies to intelligent parts management for manufacturers of vehicle components and spare parts. On the basis of a fully integrated concept for the traceability of parts in the market prescribed by law, the digital twin can be used to collect data from service cases and then use this to create analyses or simulations of potential wear and material properties in hazardous situations. EDAG provides assistance not only with corresponding concepts, but also with tracking to end of life and with feedback processes, to enable findings from after-sales, for instance, to be fed back into development.
Safety & regulations
With increasing digitalization, the risk of cyber attacks is also growing. Both the development environments and the vehicles themselves are affected. As well securing against unauthorized intrusion from the outside, a viable security strategy also involves searching for security gaps and inadequacies in the system which pose a risk to IT security. This is the task of a vulnerability management system (VM system). This helps to minimize the following risks:
- Cyber attacks: A VM system can help to identify vulnerabilities in an IT infrastructure and take effective protective measures to minimize the risk of attacks being successful
- Data loss: By identifying and eliminating security gaps and vulnerabilities in an IT infrastructure, a VM system can help to prevent the loss or compromise of data
- Compliance violations: A VM system can help to ensure that companies comply with the rules and regulations that apply to their industry and their data
Implementing effective vulnerability management calls for both the necessary expertise in cybersecurity subjects and a concept tailored to your own needs. EDAG's security specialists will help you to achieve your goals. To this end, EDAG has already developed a number of methods and processes that have proved their value in practical applications.
The second element of the security concept comprises the design and implementation of cybersecurity and data protection measures. In the race against cybercriminals, it is vital to be technically completely up-to-date and to keep an eye on the changing threat landscape and attack interfaces. What is more, the constantly changing regulatory requirements must be monitored and implemented. 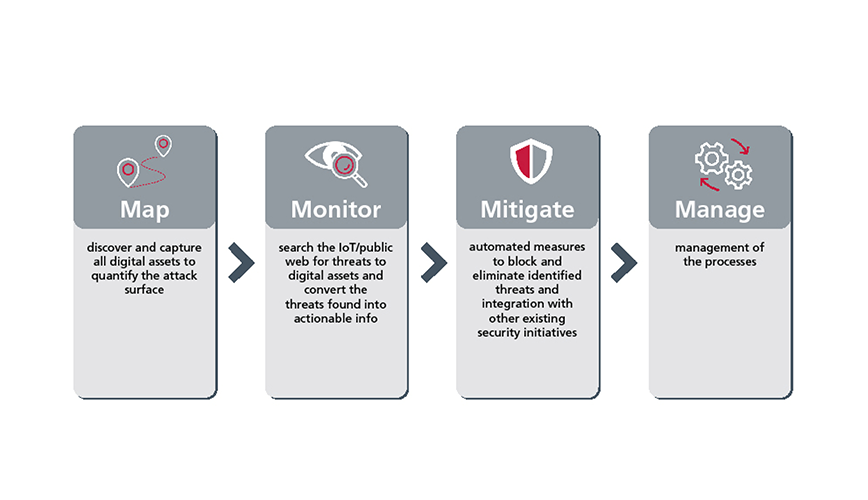
In the fields of cybersecurity and data protection, EDAG acts as an innovator for object-oriented fields of action, possible solutions and strategic topics, and as a development partner for processes and system integration. Our IT security experts offer a range of solutions and services to improve the security of companies and vehicles.
Do you have any further questions about the extensive field of digitalization in after-sales? If you do, then contact Barzin Hadjimoradi, Team Leader Product Quality & Care at EDAG Engineering. The "EDAG Aftersales Guide" contains extensive suggestions and a detailed summary of the various services offered by EDAG in this field. Download the PDF here. 





