The fully autonomous passenger car is still a long way off. However, driver assistance systems that can at least provide support are advancing at a rapid rate. Essentially, they are based on recognition of the vehicle's environment. Artificial intelligence helps ensure that they work reliably even in adverse weather conditions and if there is dirt on the cameras.
They alert the driver to speed limits, maneuver themselves into parking spaces, and intervene in dangerous situations: more and more digital assistants are becoming available to help drivers. They work on the basis of camera images or other sensors, such as radar, lidar or ultrasound.
In theory, they supply high-quality results which help to make driving safer. Unfortunately, however, the reality is often quite different. If the camera lens is contaminated by dust or dirt, or in adverse weather conditions - rain, fog or snow for instance - the software is not sent a clear image. As a result, crucial information might then be missing.
How malfunctions can be reduced
This can have serious consequences - and not only for fully automated traffic systems, since missing traffic or environmental information can also be a problem for partially automated systems. Take, for example, sign recognition: what speed limit applies - 80 or 60 km/h? Does the vehicle need to slow down, or is the speed within the permissible range? Misinterpretations in the detection or avoidance of collisions can have an even more serious impact. In the worst case, accidents can be caused by unexpected driving maneuvers being triggered by an assistance system.
Four years ago, the EDAG Group began a systematic research and development program in the field of artificial intelligence (AI), with the aim of avoiding malfunctions or the total failure of a system, and to ensure the robust, reliable operation of software-based functions and assistance systems for a wide variety of situations and environments. Image information can be improved with the help of AI, and the risk of errors in driving assistance systems reduced.
AI inspired by human memory
One of the most promising approaches to AI-based image enhancement makes use of concepts geared to the structure of the human brain and memory processes. Innovative auto-encoder architectures apply a combination of partial convolutional neural networks (pCNN) and convolutional long short-term memory networks (ConvLSTM).
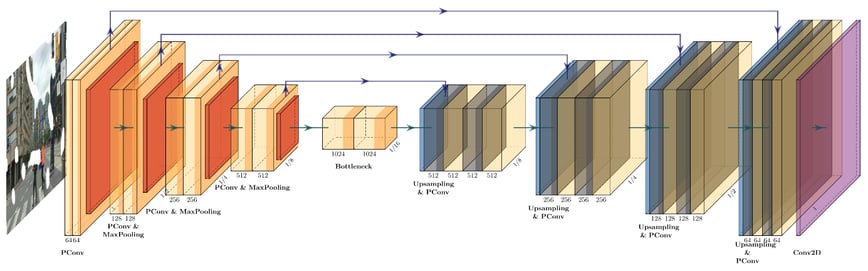
Architecture of the partial convolutional LSTM layer
An architecture of this type makes spatiotemporal feature extraction inspired by human memory possible. In order to reconstruct an incomplete image, the AI also uses information from previous and subsequent images. This deep-learning approach permits robust completion in spite of image errors, which can take a variety of different forms.
The network architecture selected is able to abstract information from objects and scenarios that have been previously seen, and then identify basic connections. For example, hidden objects in a single image can be reconstructed on the basis of empirical values from previous images. During the training process, these AI abilities are collected from millions of different images by means of analysis The correctness of the abstraction must be constantly checked during the training process.
Geared to different types of hardware
The currently developed network architecture of the artificial intelligence used for image enhancement has been optimized for the widely used Nvidia platforms for autonomous vehicles. However, it can also be run on FPGA systems by Xilinx. At all events, users can be sure that they will benefit from high-performance algorithms in combination with a standard hardware platform for embedded systems. The system can be used with rear view, front view and top view camera systems, and also in combination with other sensor types.
Numerous applications
The advantages offered by AI-assisted systems of this kind can be seen in the automotive environment, in fully automated parking for example. If part of the windshield or the rear-view camera is soiled during the parking maneuver, and this restricts the camera-based functions, the system will shift down from active to inform mode only. In this case, the vehicle will only assist the driver, and not completely take over the task of parking. With the support of the AI software, which ensures the quality and robustness of the camera images, the reduction of the assistance function from an autonomous to a purely informational support system is prevented or postponed.
Apart from its use in the automotive sector, AI-assisted image enhancement is also an interesting application for industry. It can, for instance, be used in visual quality control. Other possible applications for innovative machine and deep learning technologies include the simplification of complex FEM calculations and the qualitative evaluation of measuring signals for vehicle safety. The adaptation of AI-based architectures to the challenges concerned is generic and, thanks to the adequate data sources and the preprocessing of these, has the potential to contribute to continuous improvement and validation, be this in the optimization of internal processes or in the development of future vehicle concepts.
If you want to know more about the use of AI-assisted methods in the field of image processing, talk to our specialist Heiko Herchet, Vice President Digital Transformation. Further details concerning the development of AI architectures at EDAG, for instance convolutional neuronal networks (CNN) for image enhancement, can also be found in our white paper "Efficient Image Processing Using AI”, which can be downloaded here.






